How to Improve Fertility in Your Cattle Herd?
Fertility is one of the most critical pillars in cattle production, as it directly impacts productivity and profitability. Optimizing fertility in your herd requires an integrated approach that includes management, nutrition, health, and genetics. Here are key strategies to improve your herd’s reproductive performance:
1. Adequate Nutrition
A balanced diet tailored to the animals’ needs is essential. A lack of nutrients such as energy, protein, minerals, and vitamins can lead to delayed puberty, irregular estrous cycles, and low conception rates. Make sure to:
- Provide sufficient energy, especially for lactating cows.
- Include minerals like phosphorus, selenium, and zinc, which are crucial for fertility.
- Regularly assess body condition scores.
2. Stress Management
Stress negatively affects hormonal levels and reproductive activity. Minimize stress by:
- Offering a calm and comfortable environment.
- Reducing excessive handling and abrupt changes in the environment.
- Scheduling reproductive activities during low-stress periods, such as post-weaning.
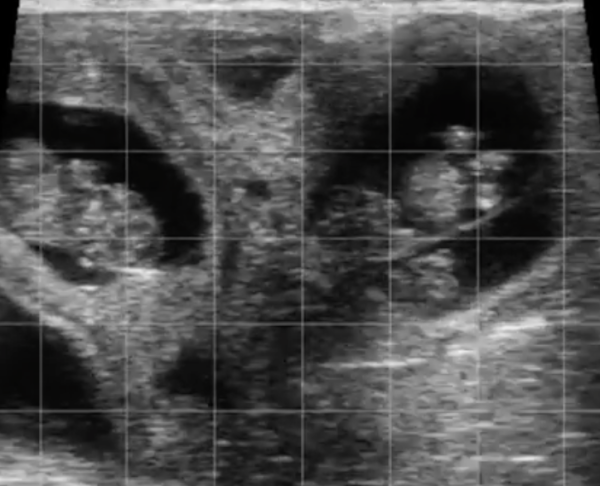
3. Reproductive Health Monitoring
Regular reproductive check-ups help detect problems such as uterine infections, ovarian cysts, or malformations. This includes:
- Performing rectal palpation or ultrasounds to monitor estrous cycles and detect pathologies.
- Implementing vaccination protocols to prevent diseases like leptospirosis and brucellosis that affect fertility.
4. Genetic Selection
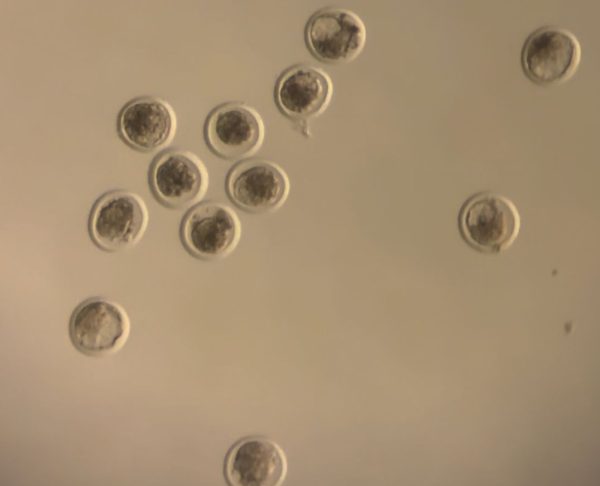
Genetic improvement is key to increasing fertility in your herd. Use bulls or semen with high genetic quality and select animals with strong reproductive records. Artificial insemination and embryo transfer are valuable tools to accelerate genetic progress.
5. Synchronization Strategies
Using estrus synchronization protocols and artificial insemination allows for better control of reproductive management. These techniques optimize resource use and improve pregnancy rates.
Conclusion
Fertility reflects the comprehensive management of your herd. By ensuring the health, nutrition, and well-being of your animals, you can maximize conception rates and achieve greater productivity in your cattle operation.
📲 Become a cattle reproduction expert! Enroll in our specialized courses and learn how to enhance your herd’s fertility.
Let me know if you’d like adjustments or more details!