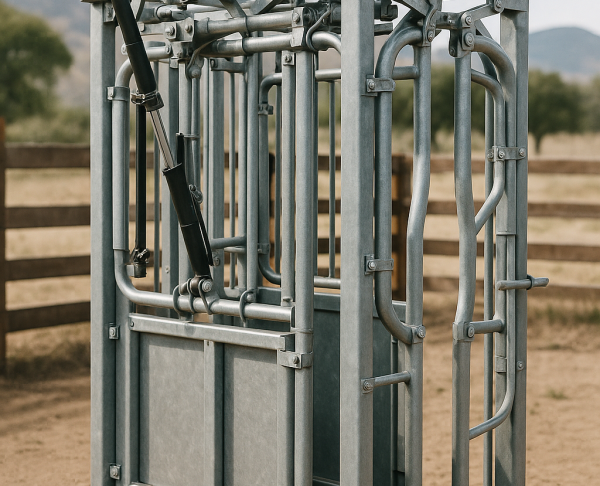
Cattle chutes are essential facilities in professional cattle farming. Their main purpose is to facilitate the safe handling of livestock, ensuring both worker safety and animal welfare.
In cattle herd management, chutes allow precise and controlled execution of procedures such as:
• Rectal palpation and reproductive ultrasound.
• Artificial insemination and embryo transfer.
• Vaccination, deworming, and medical treatments.
• Identification (ear tags, tattoos, branding, microchips).
• Minor surgical procedures (dehorning, castration).
• Hoof trimming and orthopedic corrections.
The importance of having a high-quality chute lies in the fact that it reduces animal stress, increases work efficiency, and minimizes the risk of accidents.
Below, we present the 10 key features every cattle chute should have, based on academic standards of livestock handling and animal welfare.
⸻
1. Strength and Durability
Chutes should be built from high-resistance materials such as galvanized steel or structural steel with anticorrosive coatings.
• Durability is critical as they are exposed to sun, rain, urine, and manure.
• A strong structure can withstand the force of adult cattle weighing between 500 and 1,200 kg (1,100–2,600 lbs).
• Investing in quality materials prevents frequent repairs and ensures long service life.
⸻
2. Ergonomic and Safe Design
Proper design avoids injuries and reduces animal suffering.
• Smooth surfaces without sharp edges prevent cuts or bruises.
• Alleys must be wide enough for cattle to move comfortably but narrow enough to prevent turning around.
• Solid walls (instead of open bars) help cattle move forward calmly by reducing visual distractions.
⸻
3. Efficient Restraining System
The headgate or neck clamp is the core of the chute.
• It must immobilize the animal securely without restricting breathing.
• Adjustable models allow safe handling of calves, cows, and bulls.
• Some systems feature automatic headgates that close as the animal enters, minimizing operator effort.
⸻
4. Easy Entry and Exit
A quality chute should allow:
• Smooth entry from the alley, guiding animals calmly.
• Rear safety gate to prevent backward movement.
• Quick, safe exit, reducing crowding and potential injuries.
Poor design in this area is often the main cause of accidents for both workers and cattle.
⸻
5. Adaptability to Different Types of Cattle
Handling calves, dairy cows, or breeding bulls requires different adjustments.
• Modern chutes offer height and width adjustments.
• Some models are specialized for dairy, feedlot, or reproductive management.
• Versatility is important for mixed herds.
⸻
6. Practical Operation Mechanisms
Labor effort is an important factor in chute design.
• Chutes can be manual, hydraulic, or pneumatic.
• Hydraulic systems provide greater comfort and precision, ideal for large herds.
• Manual systems, while requiring more effort, are cost-effective and widely used by small and medium producers.
A practical mechanism allows handling with fewer workers and greater safety.
⸻
7. Worker Safety
Personnel must be protected from kicks, horns, or sudden movements.
• Chutes should include emergency exits for quick operator escape.
• Side access doors allow handling without direct exposure.
• Protective bars and locking systems reduce accident risks.
⸻
8. Versatility in Handling
A chute should not be limited to a single function.
• Side access points allow reproductive exams, hoof trimming, and sample collection.
• Adjustable windows facilitate vaccination and drug administration.
• Some chutes include platforms for minor surgical procedures.
This makes the chute a complete livestock handling station.
⸻
9. Stress Reduction in Cattle
Low-stress handling is increasingly adopted in modern cattle production.
• Curved alleys simulate natural herd movement.
• Solid walls prevent external distractions.
• Progressive flow of cattle avoids sudden movements or crowding.
Lower stress in cattle results in:
• Fewer injuries.
• Stronger immune response.
• Better reproductive and productive performance.
⸻
10. Cost-Benefit Balance
Although a chute may seem like a high initial investment, the economic return is significant:
• Fewer losses from injuries or accidents.
• Reduced need for large numbers of workers.
• Improved efficiency in health and reproductive programs.